Picking the Ideal Cybersecurity Automation Tool in 2023
The rapid evolution of the digital landscape has ushered in unprecedented challenges for organizations, making it imperative to stay one step ahead of cyber threats. The implementation of hybrid work models, the rise of cloud usage, and the proliferation of edge devices have expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals to exploit. As a result, cybersecurity professionals are realizing the need to adopt a more preventative and proactive approach to safeguard their core business operations.
The Need for Cybersecurity Automation
According to recent studies, the global average cost of a data breach reached $4.35 million in 2023, compared to that, it was a staggering $9.44 million in the United States. Evidently highlighting the financial impact that cyberattacks can have on organizations.
To combat this growing threat landscape, executives across industries are turning to artificial intelligence (AI) as a security tool. In fact, a significant majority—64% of respondents globally—are already implementing AI for security capabilities, with an additional 29% evaluating its implementation.
In this article, we will provide organizations with a comprehensive understanding of the benefits of implementing automation solutions, how they can enhance security posture, and the various types of cybersecurity automation tools available. By embracing automation, organizations can proactively detect and respond to threats, streamline security processes, and fortify their defenses against emerging risks.
Traditional IT Security vs. Automated Cybersecurity
Traditional IT security measures have been the go-to for organizations in protecting their technology ecosystems. These measures encompass a wide range of strategies, including network security, endpoint security, cloud security, and more. While they have been effective to some extent, they do come with their fair share of limitations and challenges:
- Manual execution of security tasks: Security teams have to manually perform tasks, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error.
- Delayed response to emerging threats: Traditional security approaches may struggle to keep up with the rapidly evolving threat landscape, resulting in delayed detection and response.
- Lack of scalability: As organizations grow and their technology ecosystems expand, it becomes increasingly challenging to scale traditional security measures effectively.
Cybersecurity Automation: Doing More with Less
Enter automated cybersecurity, a complementary approach that harnesses the power of technology to streamline security operations and enhance overall defense capabilities. Automation empowers organizations to automate repetitive and routine tasks, freeing up valuable time and resources for IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. By leveraging automation, organizations can overcome the limitations of traditional security measures and achieve the following benefits:
- Enhanced threat detection and response: Automation enables real-time monitoring and rapid response to potential threats, improving the organization’s ability to detect and mitigate risks promptly.
- Consistent and reliable execution: With automated processes, the risk of human error is significantly reduced, ensuring consistent and reliable execution of security protocols.
- Improved efficiency and scalability: Automation allows organizations to scale their security operations seamlessly, adapting to the evolving needs of the business without sacrificing effectiveness.
- Proactive security measures: Automated cybersecurity solutions can proactively identify vulnerabilities, apply security patches, and implement preventive measures to minimize the risk of breaches.
However, it’s important to note that automation alone is not a silver bullet.
The synergy between manual and automated security measures is crucial for a comprehensive cybersecurity infrastructure. While automation takes care of routine tasks and accelerates response times, human expertise is still indispensable for complex decision-making, strategic planning, and addressing unique and emerging threats.
By combining the strengths of both approaches, organizations can create a robust security framework that maximizes protection while optimizing operational efficiency.
Signs That Your Organization Needs Cybersecurity Automation
Increased frequency and severity of data breaches
According to the 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report, published by Verizon, there has been a significant increase in data breaches globally. The report highlights that data breaches have become more frequent and severe, posing a growing threat to organizations. This emphasizes the importance of implementing robust cybersecurity measures.
Slowing incident response times
Timely detection and remediation of security incidents are critical to minimizing the impact of breaches. However, a study by NIST found that the mean-time-to-detect (MTTD) and mean-time-to-remediate (MTTR) incidents has been increasing across organizations. If your incident response times are slowing down, it’s a clear indication that your security apparatus needs improvement.
Overwhelmed by false positives
False positives in security alerts can divert valuable time and resources, causing alert fatigue and reducing the efficiency of your security team.
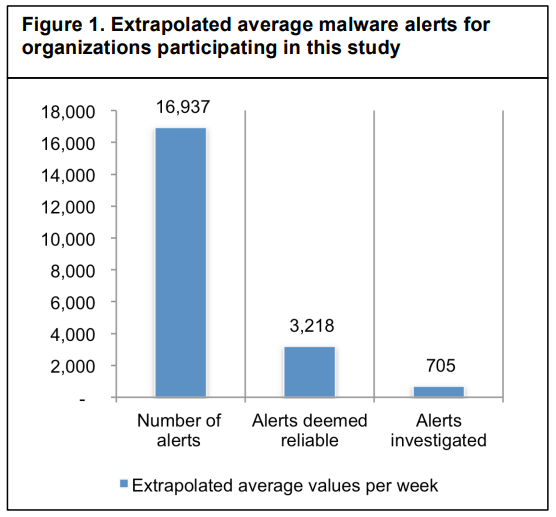
The Ponemon Institute’s research indicates that organizations receive an average of 17,000+ false-positive alerts per week, with analysts spending up to 25% of their time investigating and addressing them. If your security team is overwhelmed by false positives, it’s a sign that automation can help improve efficiency.
Alert fatigue and resource constraints
Cybersecurity professionals face immense pressure to keep up with evolving threats and maintain a robust defense posture. However, resource constraints can hinder their ability to tackle emerging challenges effectively.
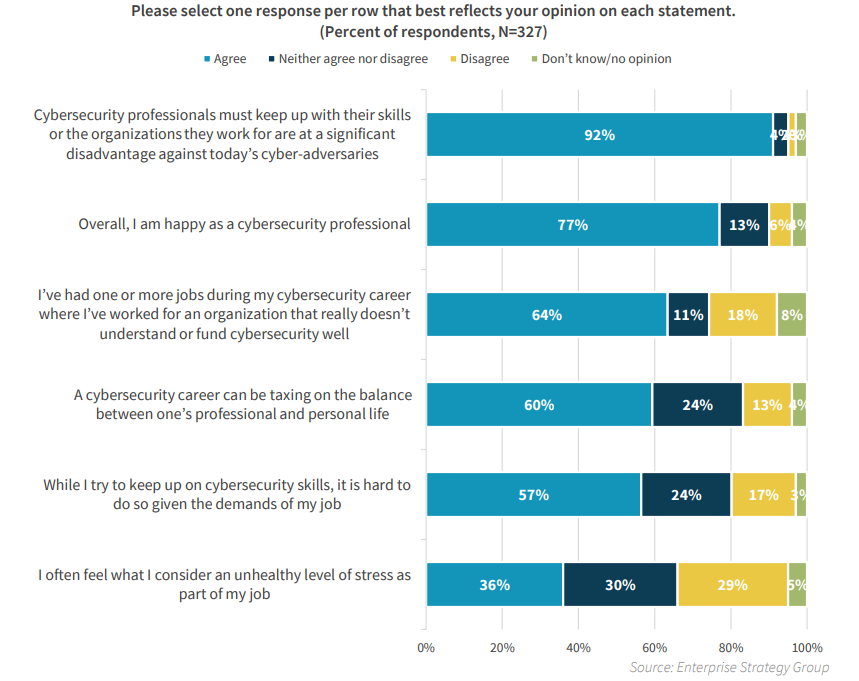
A survey conducted by the Information Systems Security Association (ISSA) revealed that 62% of organizations reported a shortage of skilled cybersecurity personnel. If your security team feels overwhelmed, experiences alert fatigue, or lacks sufficient time and resources to proactively address threats, security automation can alleviate these burdens.
Different Types of Cybersecurity Automation Tools
To effectively implement security automation, organizations can leverage various tools and technologies designed to streamline security operations, enhance threat detection and response capabilities, and automate repetitive tasks. Here are some common types of cybersecurity automation tools:
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools
SIEM tools enable organizations to aggregate and analyze log and event data from diverse sources such as applications, devices, networks, infrastructure, and systems. They provide a centralized view of an organization’s IT environment, facilitating real-time threat monitoring, incident response, and compliance management. SIEM solutions help organizations identify patterns, detect anomalies, and correlate events to identify potential security incidents accurately.
Benefits of SIEM Tools:
- Streamline visibility and monitoring across the IT environment.
- Improve incident response capabilities through real-time alerts and notifications.
- Enhance compliance management by generating audit trails and reports.
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) Tools
SOAR tools streamline security operations by automating and orchestrating tasks related to threat management, incident response, and security operations. These tools integrate with various security technologies and systems, allowing organizations to create standardized playbooks and automated workflows for incident response and mitigation.
Benefits of SOAR Tools:
- Accelerate incident response by automating repetitive tasks.
- Enhance collaboration and coordination among security teams.
- Improve efficiency and consistency in incident management and resolution.
Vulnerability Management Tools
Vulnerability management tools automate the process of identifying, classifying, and prioritizing vulnerabilities in an organization’s IT infrastructure. These tools scan networks, systems, and applications to discover vulnerabilities, assess their severity, and recommend remediation activities. By automating vulnerability management, organizations can proactively address security weaknesses and reduce the window of exposure to potential attacks.
Benefits of Vulnerability Management Tools:
- Identify and prioritize vulnerabilities in a timely manner.
- Streamline the remediation process through automated recommendations.
- Improve overall security posture by proactively addressing vulnerabilities.
Endpoint Protection Tools
Endpoint protection tools focus on securing individual endpoints, such as PCs, laptops, mobile devices, and IoT devices, from various threats, including malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access. These tools typically include features like antivirus, anti-malware, firewall, and device management capabilities, providing comprehensive protection for endpoints.
Benefits of Endpoint Protection Tools:
- Detect and mitigate threats at the endpoint level.
- Monitor and manage endpoint security centrally.
- Protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA technology involves the use of software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks that do not require complex analysis. While RPA is not specifically designed for cybersecurity, it can be utilized to perform certain security tasks, such as vulnerability scanning, running monitoring tools, and basic threat mitigation. RPA can execute predefined tasks based on specific triggers or schedules.
Benefits of RPA Technology
- Automate routine security tasks and processes.
- Improve efficiency by reducing manual effort and human error.
- Increase scalability and speed of security operations.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
XDR solutions represent the evolution of endpoint detection and response (EDR) and network detection and response (NDR) tools. They consolidate data from various security sources, including endpoints, networks, and cloud systems, to provide a holistic view of the organization’s security posture. XDR leverages advanced analytics, machine learning, and automation to detect and respond to sophisticated threats.
Benefits of XDR Solutions:
- Provide comprehensive threat detection and response capabilities.
- Automate threat correlation and attack investigation.
- Enable faster incident response and mitigation through centralized management.
How to Get Started with Cybersecurity Automation
To embark on your journey of cybersecurity automation, follow these essential steps:
1) ASSESSING YOUR ORGANIZATION’S NEEDS
This is another crucial step. Before implementing automation, conduct a thorough assessment of your organization’s specific cybersecurity needs. Identify the areas where automation can bring the most significant impact, such as vulnerability management, incident response, threat intelligence, or compliance management.
2) SETTING CLEAR GOALS AND OBJECTIVES
Define clear goals and objectives for your cybersecurity automation initiative. These goals could include reducing incident response time, improving threat detection capabilities, enhancing compliance management, or increasing operational efficiency. Ensure that the goals align with your organization’s overall cybersecurity strategy. Try to include specific KPI’s and end results.
3) DESIGNING YOUR AUTOMATION STRATEGY
Develop a comprehensive automation strategy that outlines the specific use cases, tools, and processes to be automated. Consider factors such as resource allocation, budget requirements, and timeline for implementation. Collaborate with key stakeholders, including IT, security teams, and senior management, to ensure alignment with overall organizational goals. Your
4) PILOTING AND TESTING
Start with a pilot implementation of the automation solution in a controlled environment. This allows you to validate the effectiveness of the chosen tools and processes and identify any necessary adjustments before scaling up to the entire organization. Conduct thorough testing and evaluation to ensure the desired outcomes are achieved.
5) TRAINING AND SKILL DEVELOPMENT
Invest in training and skill development for your cybersecurity and IT teams to ensure they have the necessary knowledge and expertise to effectively utilize the automation tools and workflows. This will enable them to maximize the benefits of automation and adapt to new processes and technologies.
6) MONITORING AND EVALUATION
Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of your cybersecurity automation implementation. Regularly assess key metrics such as incident response time, threat detection rate, and overall security posture to measure the impact of automation on your organization’s security operations. Use these insights to make necessary adjustments and improvements.
Selecting the Right Service Provider
Choosing a reputable service provider is crucial for the successful implementation of cybersecurity automation. Consider the following factors:
- Experience or Expertise: Seek a service provider with a proven track record in cybersecurity automation. Look for their expertise in addressing the specific challenges and requirements of your industry.
- Comprehensive Solutions for your Particular Use Case: Assess whether the provider offers a comprehensive suite of automation tools that align with your organization’s needs. Look for solutions covering SIEM, SOAR, vulnerability management, and endpoint protection.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure that the provider’s automation solutions can seamlessly integrate with your existing security infrastructure, including firewalls, antivirus software, and network monitoring tools.
- Scalability & Flexibility: Consider the provider’s ability to scale the automation solution as your organization grows and adapts to evolving threats. Flexibility in customization and future expansion is vital.
- Support & Maintenance: Evaluate the provider’s support services and ongoing maintenance offerings. Prompt assistance and regular updates are crucial for effective automation implementation.
Remember, automation is an ongoing process that requires adaptability and continuous improvement to stay ahead of evolving threats and enhance your overall security posture.
Security Automation Tools and Use-Cases Chart
The following table highlights various use cases in cybersecurity automation and the corresponding ideal cybersecurity automation tools for each use case.
| Problem Area | Description | Ideal Cybersecurity Automation Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Incident Response | Streamlining incident response processes and reducing mean time to detect and remediate security incidents. | Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) |
| Vulnerability Management | Automating the identification, classification, prioritization, and remediation of vulnerabilities in IT resources. | Vulnerability Management Tools |
| Threat Detection | Enhancing the detection and identification of potential threats and anomalies across the organization’s IT infrastructure. | Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) |
| Compliance Management | Automating compliance-related tasks, such as data privacy regulations, industry standards, and internal policies. | Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) or Vulnerability Management Tools |
| Endpoint Protection | Ensuring comprehensive protection and monitoring of endpoints, including PCs, IoT devices, and cloud-based applications. | Endpoint Protection Tools |
| Threat Intelligence | Gathering, analyzing, and integrating external threat intelligence to proactively detect and respond to emerging threats. | Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) or eXtended Detection and Response (XDR) |
| Security Operations | Automating routine security operations tasks, such as log analysis, incident ticketing, and security workflows. | Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) |
| Network Security | Automating network monitoring, traffic analysis, and firewall rule management to strengthen network security and prevent unauthorized access. | Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) |
| Data Loss Prevention | Automating the detection, monitoring, and prevention of unauthorized data access, leakage, or theft across the organization’s network and endpoints. | Endpoint Protection Tools or Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) |
| Threat Hunting | Proactively searching for advanced threats and malicious activities within the organization’s network and systems. | Extended Detection and Response (XDR) |
Please note that the above table provides general guidance, and the ideal automation tool may vary based on the specific requirements and preferences of an organization. It is advisable to conduct a thorough evaluation of available automation tools and assess how well they align with your organization’s needs before making a final decision.
Conclusion
As hackers increasingly leverage AI and other generative technologies for malicious purposes, it is crucial for security practices to evolve and incorporate the latest automation tools and techniques to stay competitive and efficient.
At Caplock Security, we understand the importance of embracing automation to protect your organization from emerging cyber threats. Our automated XDR services offer comprehensive threat detection and response capabilities, consolidating data from across your environment to provide a holistic view of potential attacks. With our zero trust assessment and implementation services, we help organizations establish a robust security framework that safeguards critical assets and ensures granular access control.
Contact us today to learn more about how our automated security services, XDR solutions, zero trust assessment and implementation, and NIST RMF compliance expertise can fortify your organization’s cybersecurity defenses. Secure your future with Caplock Security.